JupyterHub, a multi-user Hub, spawns, manages, and proxies multiple instances of the single-user Jupyter notebook server. Here is a setup guide for using Pyenv + Anaconda on the AWS EC2.
AWS setup
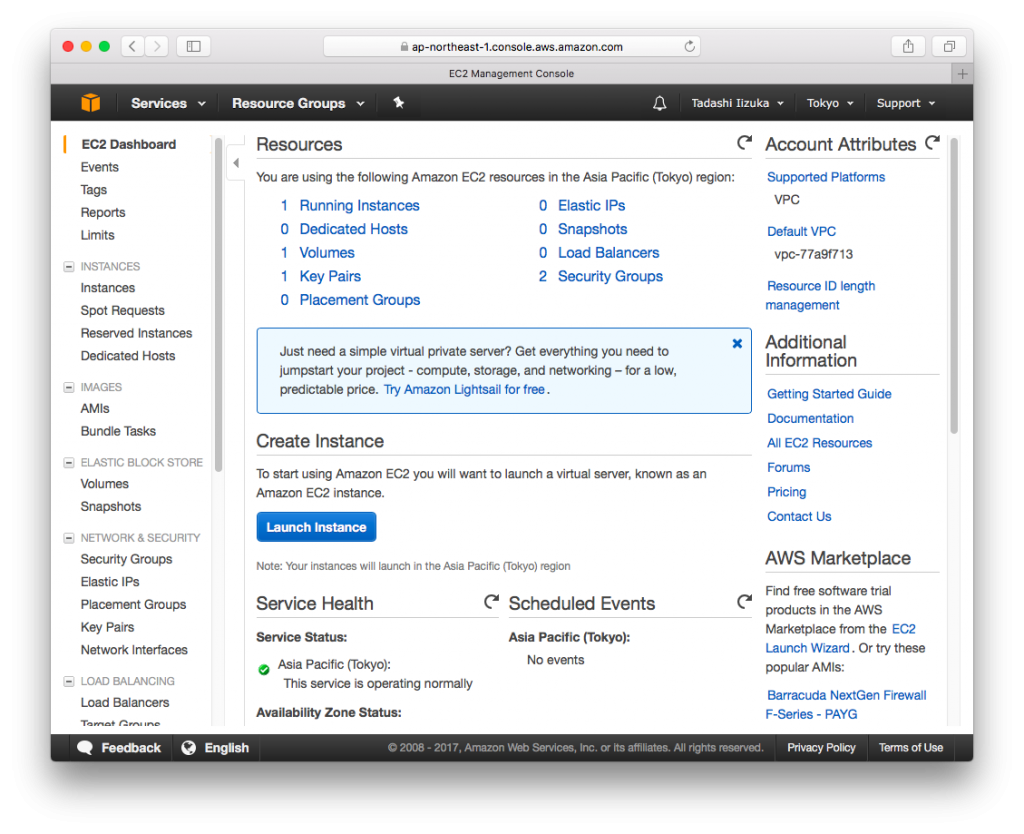
- Login to the AWS console, and selected EC2 Dashboard, Click [Launch instance]
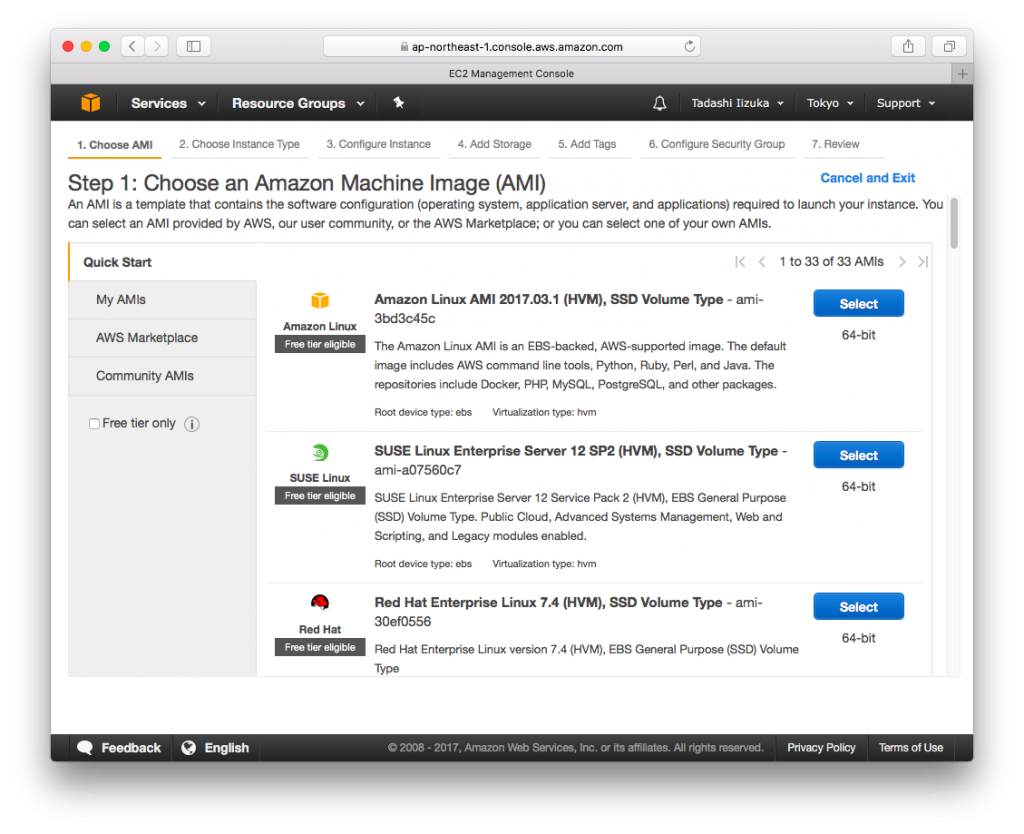
- Amazon Linux AMI 2017.03.1 (HVM), SSD Volume Type Click [Select]
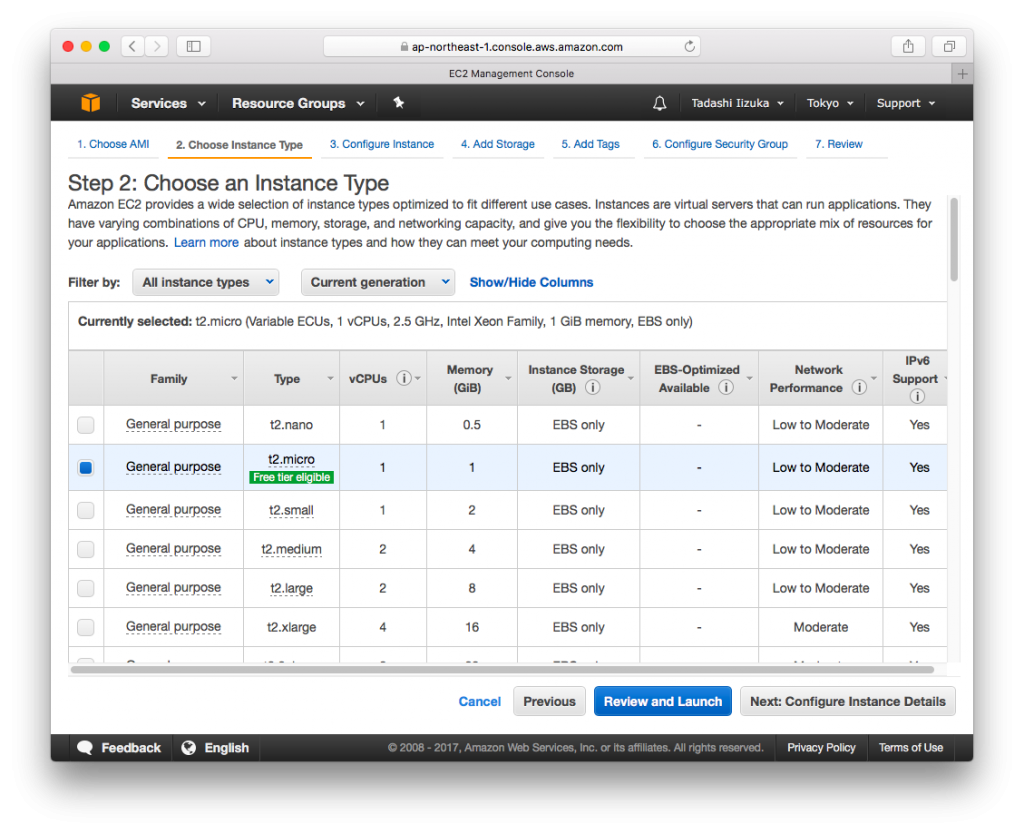
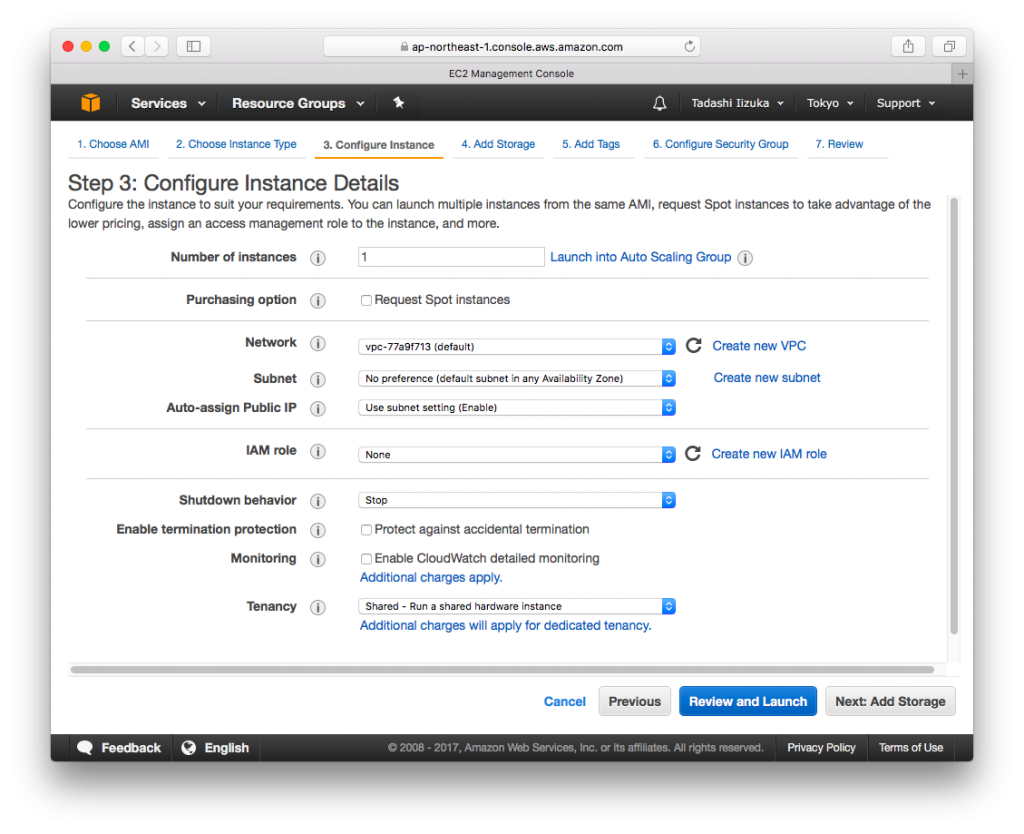
- Select the t2.micro (Free tier eligible) , Click [Next: Configure Instance Details]
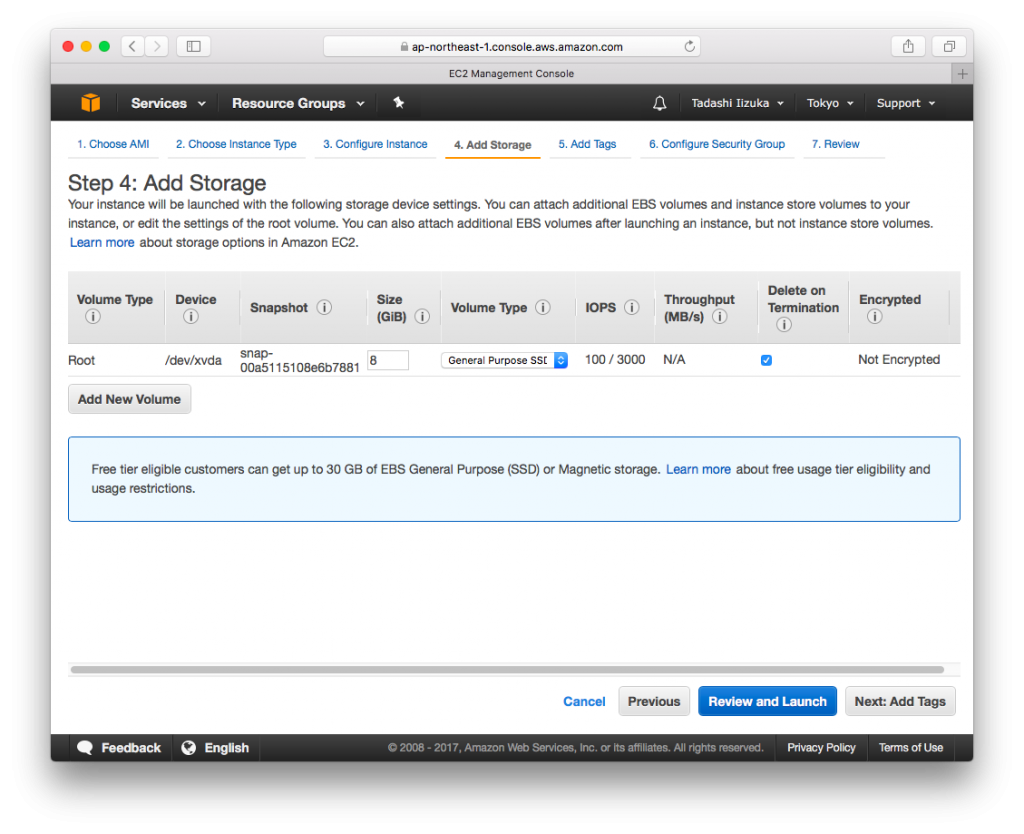
- Click [Next: Add Storage]
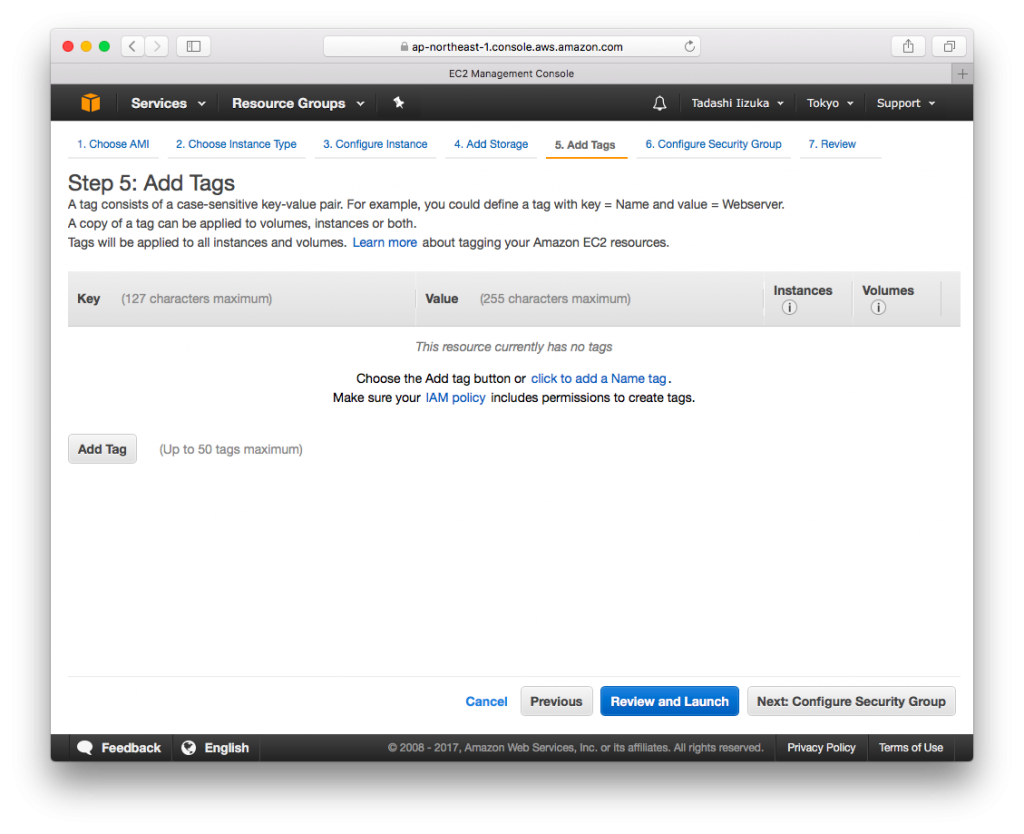
- Click [Next: Add Tags]
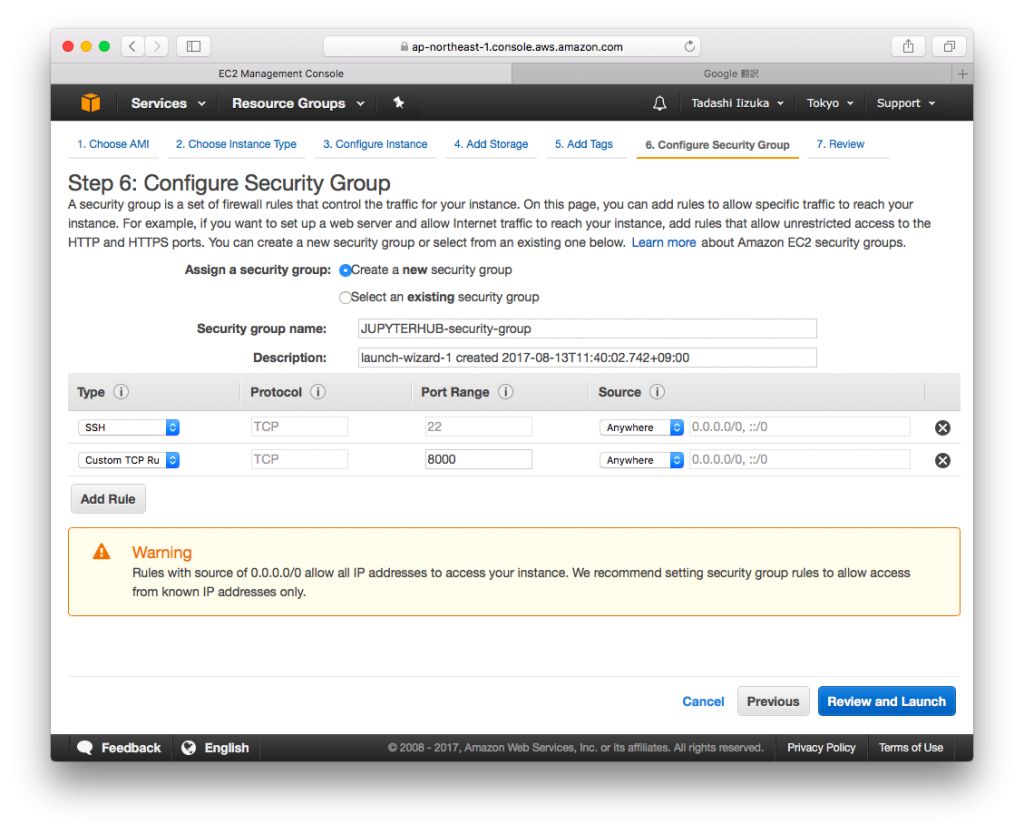
- Click [Next: Configure Security Group]
- Create a new security group, change [Security group name:] as you want, Add Type, SSH, Custom TCP Rule, as below. Then Click [Review and Launch]
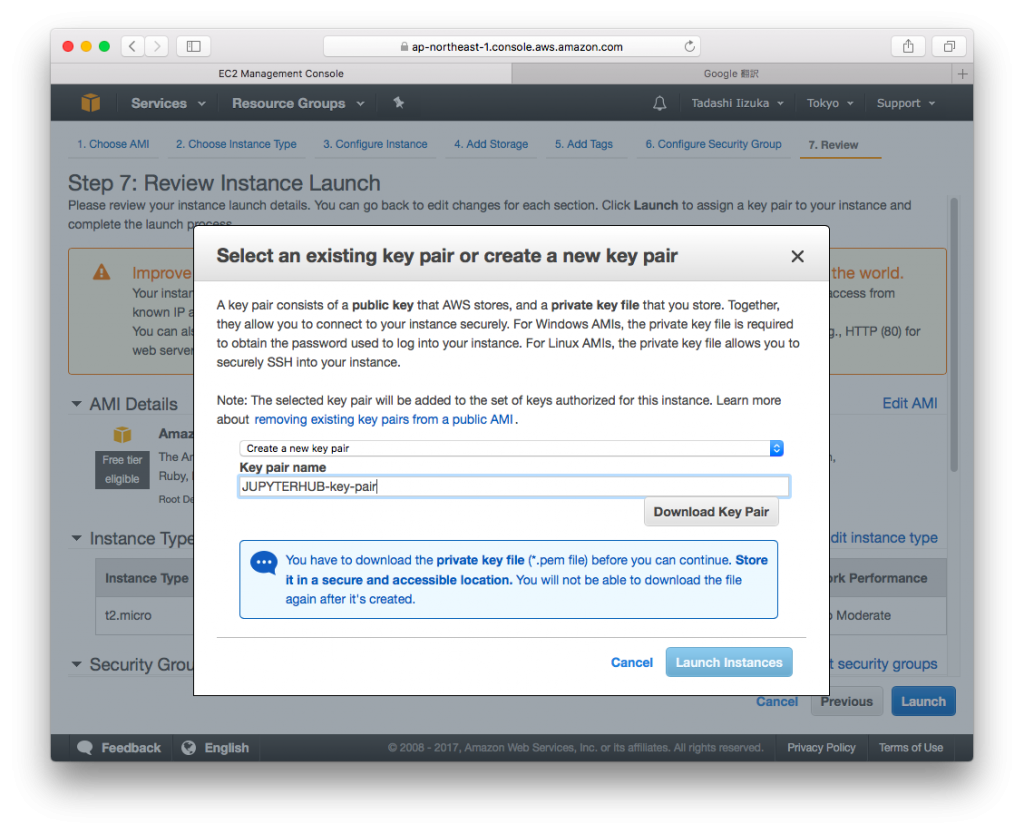
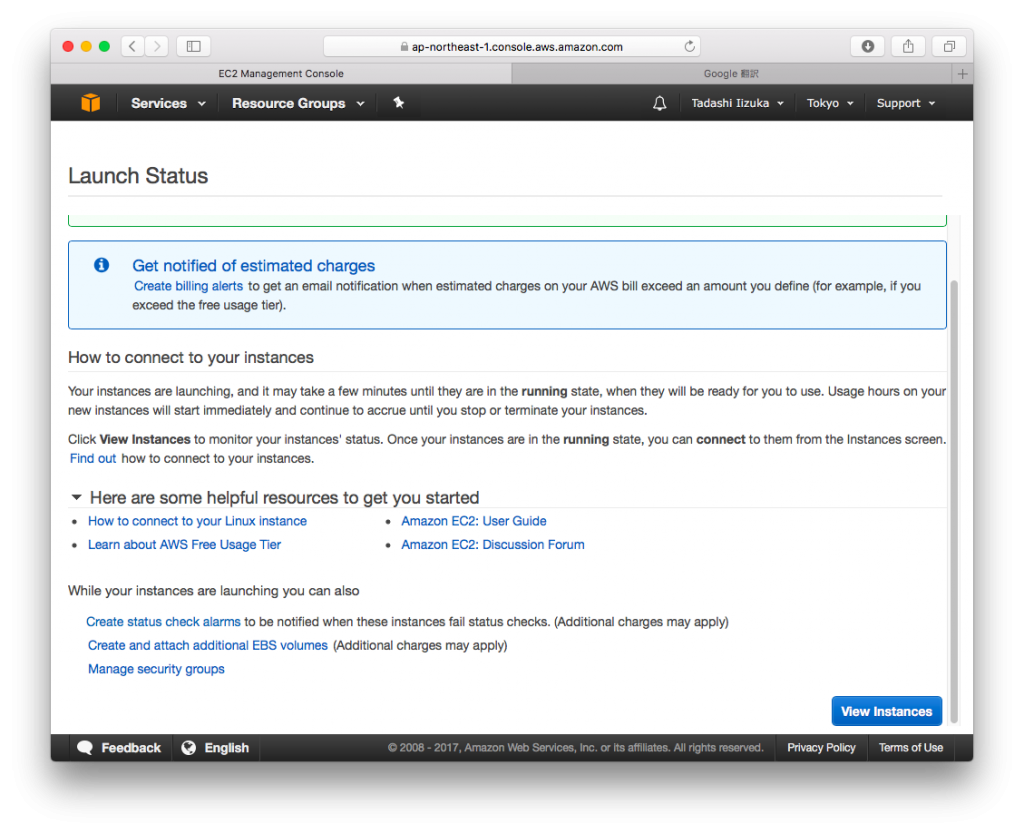
- Click [Launch], Create a new key pair, Input [Key pair name] as you want, then Click [Download Key Pair], Then Click [Launch Instances]
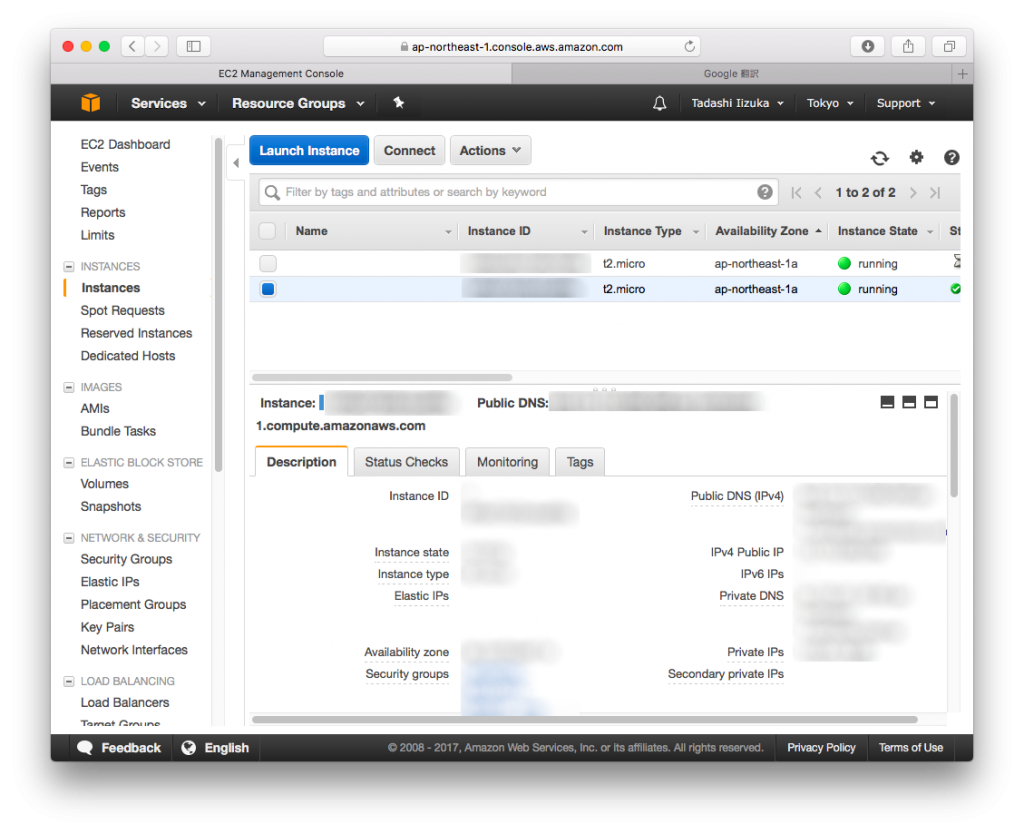
- Click [View Instances]
- Wait for a while utile the Status Check will be changed to the “2/2 checks passed”. AWS EC2 setup has completed. “Public DNS (IPv4)” will be used for SSH Login.
Pyenv setup
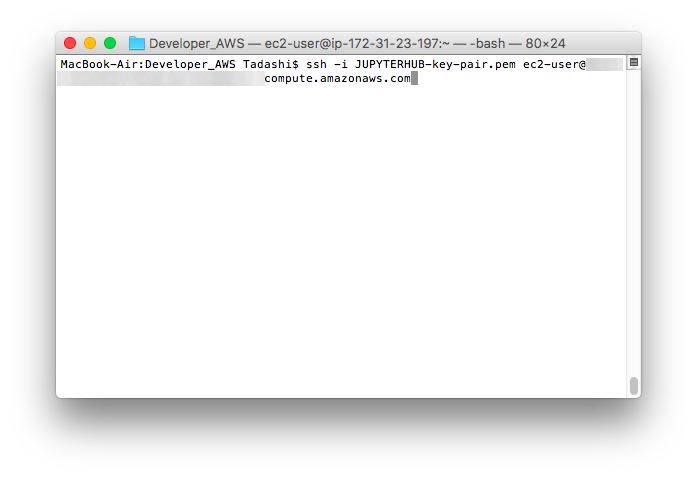
- ssh -i JUPYTERHUB-key-pair.pem ec2-user@[Public DNS(IPv4)]
$ sudo yum update
$ sudo su
# yum install gcc gcc-c++ make git openssl-devel bzip2-devel zlib-devel readline-devel sqlite-devel
# cd /opt
# git clone https://github.com/yyuu/pyenv.git pyenv
# echo 'export PYENV_ROOT="/opt/pyenv"' >> ~/.bashrc
# echo 'if [ -d "${PYENV_ROOT}" ]; then' >> ~/.bashrc
# echo ' export PATH=${PYENV_ROOT}/bin:$PATH' >> ~/.bashrc
# echo ' eval "$(pyenv init -)"' >> ~/.bashrc
# echo 'fi' >> ~/.bashrc
# exec $SHELL -l
Anaconda install
# pyenv install anaconda3-4.4.0 # pyenv global anaconda3-4.4.0 # python --version Python 3.6.1 :: Anaconda 4.4.0 (64-bit)
JupyterHub install
# conda install -c conda-forge jupyterhub # conda install notebook
JupyterHub setup
# mkdir /etc/jupyterhub # cd /etc/jupyterhub # jupyterhub --generate-config # vi jupyterhub_config.py #c.Spawner.notebook_dir = '' c.Spawner.notebook_dir = '~/notebook'
Startup setup
# echo jupyterhub -f /etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub_config.py > jupyterhub.sh # echo su -l root /etc/jupyterhub/jupyterhub.sh \& >>/etc/rc.local
JupyterHub user setup
# adducer testuser # passwd testuser Changing password for user testuser. New password: Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. # reboot * ssh -i JUPYTERHUB-key-pair.pem ec2-user@[Public DNS(IPv4)] $ mkdir notebook $ sudo passed ec2-user Changing password for user ec2-user. New password: Retype new password: passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. $ sudo su - testuser $ mkdir notebook
Check whether can login
- http://[Public DNS(IPv4)]:8000
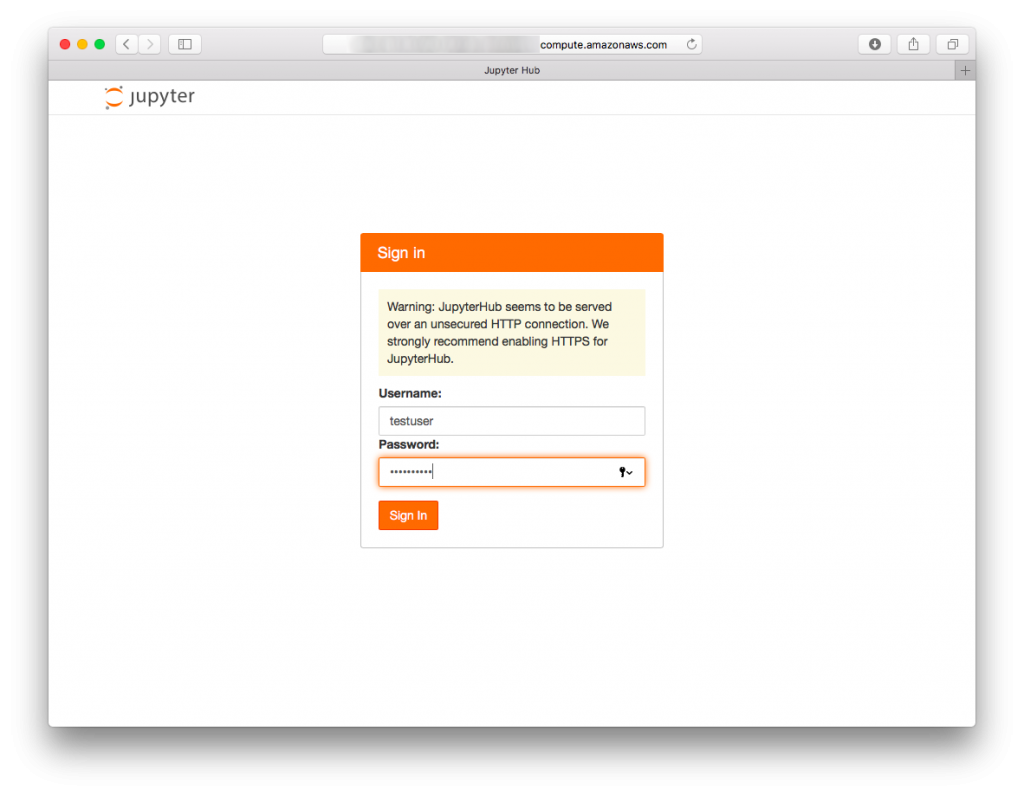
- Login completed
If you can see like this screen, all setup has been completed. After completed setup, you can add additional user by using “adduser” command.